PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The glycopeptides vancomycin and teicoplanin are clinically important antibiotics. The carbohydrate portions of these molecules affect biological activity, and there is great interest in developing efficient strategies to make carbohydrate derivatives. To this end, genes encoding four glycosyltransferases, GtfB, C, D, E, were subcloned from Amycolatopsis orientalis strains that produce chloroeremomycin (GtfB, C) or vancomycin (GtfD, E) into Escherichia coli. After expression and purification, each glycosyltransferase (Gtf) was characterized for activity either with the aglycones (GtfB, E) or the glucosylated derivatives (GtfC, D) of vancomycin and teicoplanin. GtfB efficiently glucosylates vancomycin aglycone using UDP-glucose as the glycosyl donor to form desvancosaminyl-vancomycin (vancomycin pseudoaglycone), with kcat of 17 min-1, but has very low glucosylation activity, e 0.3 min-1, for an alternate substrate, teicoplanin aglycone. In contrast, GtfE is much more efficient at glucosylating both its natural substrate, vancomycin aglycone (kcat ) 60 min-1), and an unnatural substrate, teicoplanin aglycone (kcat ) 20 min-1). To test the addition of the 4-epi-vancosamine moiety by GtfC and GtfD, synthesis of UDP-��-L-4-epi-vancosamine was undertaken. This NDP-sugar served as a substrate for both GtfC and GtfD in the presence of vancomycin pseudoaglycone (GtfC and GtfD) or the glucosylated teicoplanin scaffold, 7 (GtfD). The GtfC product was the 4-epi-vancosaminyl form of vancomycin. Remarkably, GtfD was able to utilize both an unnatural acceptor, 7, and an unnatural nucleotide sugar donor, UDP- 4-epi-vancosamine, to synthesize a novel hybrid teicoplanin/vancomycin glycopeptide. These results establish the enzymatic activity of these four Gtfs, begin to probe substrate specificity, and illustrate how they can be utilized to make variant sugar forms of both the vancomycin and the teicoplanin class of glycopeptide antibiotics. (http://walsh.med.harvard.edu/)
Vancomycin is a member of the glycopeptide class of antibiotics. Vancomycin resistance (van) gene clusters are found in human pathogens such as Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium and Staphylococcus aureus, glycopeptide-producing actinomycetes such as Amycolotopsis orientalis, Actinoplanes teichomyceticus and Streptomyces toyocaensis and the nonglycopeptide producing actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor. Expression of the van genes is activated by the VanS/ VanR two-component system in response to extracellular glycopeptide antibiotic. Two major types of inducible vancomycin resistance are found in pathogenic bacteria; VanA strains are resistant to vancomycin itself and also to the lipidated glycopeptide teicoplanin, while VanB strains are resistant to vancomycin but sensitive to teicoplanin. Here we discuss the enzymes the van genes encode, the range of diff erent VanS/ VanR two-component systems, the biochemistry of VanS/ VanR, the nature of the eff ector ligand(s) recognised by VanS and the evolution of the van cluster. (http://www.jic.ac.uk/)
Glycopeptides
|
Product |
CAS RN. |
| Actinoidins | 39319-82-9 |
| Aplysianin A | 105521-56-0 |
| Bleomycin | 11056-06-7 |
| Chloroorienticin A | 118395-73-6 |
| Chloroorienticin B | 118373-81-2 |
| Chloroorienticin C | 118373-82-3 |
| Chloroorienticin D | 118373-83-4 |
| Chloroorienticin E | 118373-84-5 |
| N-Demethylvancomycin | 91700-98-0 |
| Orienticin B | 111073-19-9 |
| Orientiparcin | 111073-20-2 |
| Peplomycin | 68247-85-8 |
| Teicoplanin | 61036-62-2 |
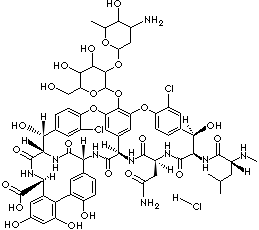
Vancomycin, a tricyclic glycopeptide, is an antibiotic produced by the soil bacillus Streptomyces orientalis, which is effective against gram-positive bacteria, especially effective highly against cocci resistant to other antibiotics. Glycopeptide antibiotics (such as decaplanin, ramoplanin, teicoplanin, vancomycin) acts by disorganizing cell membrane integrity of glycopeptide polymerization. Vancomycin acts by hindering cell-wall synthesis by blocking glycopeptide polymerization and thus are not active against gram-negative bacteria but powerful antibiotics against gram-positive bacteria. The hydrochloride salt of vancomycin is a light brown, hygroscopic powder; administered intravenously or by intravenous infusion.
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies
ASSAY
WATER
5.0% max
10ppm max
STERILITY
Sterile